
A Third of Eligible Migraine Patients Were Not Offered preventive therapy
Find out why a third of eligible migraine patients were not offered preventive therapy and
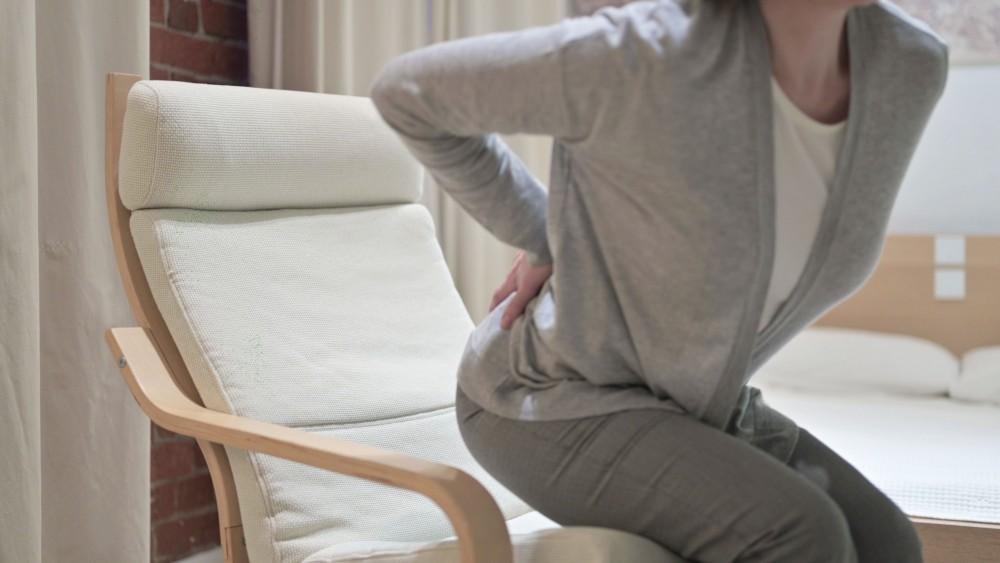

Spinal stenosis is a common condition that occurs when spaces in the spinal canal narrow and create pressure, “pinching” the spinal cord and nerve root. This can result in pain, cramping, weakness and numbness in the lower back (lumbar stenosis) and the neck (cervical stenosis), or less often, in the shoulder and arms.
The condition is caused by osteoarthritis of the spinal column and discs between the vertebrae. Other causes include a thickening of the ligaments in the back, bulging of the discs in the vertebrae, tumors, and spinal injuries.
Symptoms vary depending on the location of the nerves that are affected:
Numbness, weakness or tingling in the hand, arm, foot or leg
Problems with walking and maintaining balance
Neck pain
In severe cases, bowel or bladder dysfunction (urinary urgency and incontinence)
Pain or cramping in one or both legs
Back pain
Diagnosis is made by a thorough evaluation by a neurologist, and includes a physical evaluation, review of symptoms, as well as diagnostic testing including X-ray, CT scan, MRI scan, and electromyogram (EMG).
Treatment options for spinal stenosis include:
The exact course of treatment will depend on your specific medical needs. Pain management may include several of these methods in order to provide each patient with the level of support they need
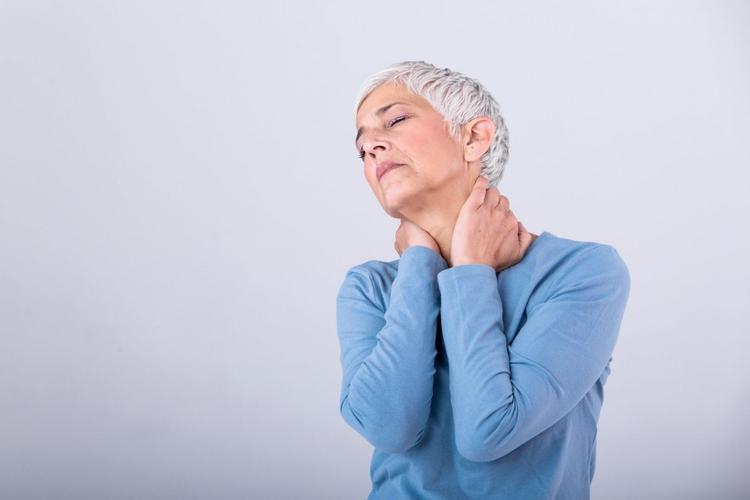

Some people with spinal stenosis may not experience symptoms. Spinal stenosis can worsen over time and can cause permanent feeling of numbness, weakness, balance problems, incontinence, and paralysis.
The risk of developing spinal stenosis increases if you
Or if you have medical conditions including:
Schedule a consultation with a Spinal Stenosis specialist today by calling (646) 679-6609 or requesting an appointment below.
See Also:
NY Neurologists

A Third of Eligible Migraine Patients Were Not Offered preventive therapy
Find out why a third of eligible migraine patients were not offered preventive therapy and
New NYNA Tourette Syndrome Study
Learn how NY Neurology Associates is advancing Tourette syndrome care with innovative treatments and a

Seizures: Understanding and Overview
Discover what causes seizures, how to recognize key symptoms, and the steps that help keep
